More about GIIMs Software Engineering Program

After successful completion of this program, candidates will also receive an ICCP or IOA Certification!!!





The demand for personalized software solutions across various industries makes software development an extremely lucrative skill. Whether it’s creating custom CRM systems or developing unique data management tools, candidates completing this GIIM program will be equipped to deliver tailored solutions that can generate substantial incomes. Equally important is the ability to debug and ensure the software runs smoothly. This remains true, even with the use of AI.
While some experts believe AI will reshape or even replace aspects of a software engineer’s job, others predict that demand for software engineers and developers will continue to grow in the coming years. Historically, technological advancements—from the rise of personal computers to the explosion of mobile devices—have only increased the need for software engineers. Though AI can automate routine tasks, engineers will shift their focus to designing systems and solving more complex challenges.
Despite the promising long-term outlook, hiring in the profession has declined since the pandemic. ADP data indicates that as of January 2024, the U.S. employed fewer software engineers than it did six years prior. However, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) forecasts strong job growth, projecting a 17% increase in software developer positions from 2023 to 2033—adding 327,900 new jobs. In 2023, the median annual salary for software developers was $130,160, according to BLS data.

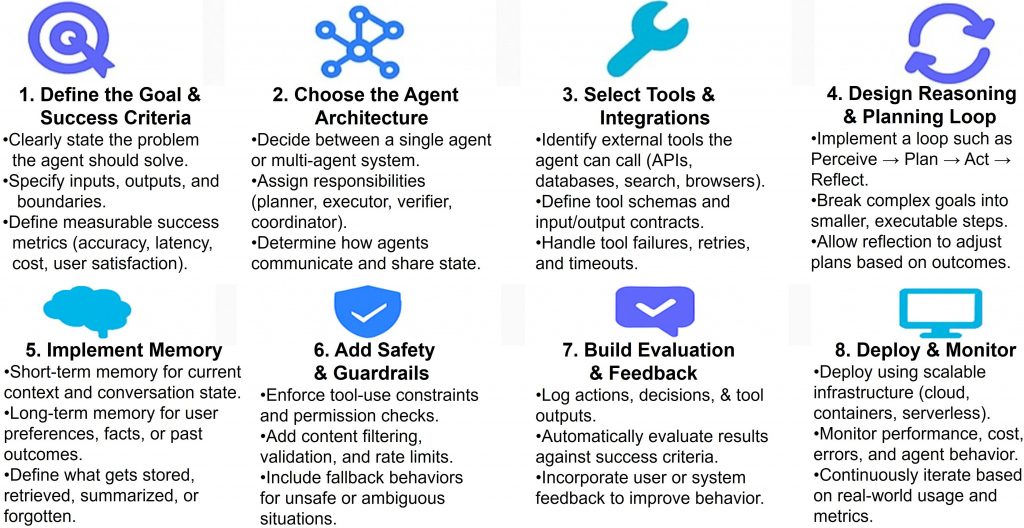
Generative AI is no longer a frontier technology. It is a strategic lever reshaping the software industry. What was once a specialized capability is now a core competency, redefining how products are built, how teams operate, and how organizations compete.
The traditional software development cycle (long planning phases, multi-week sprints) has been compressed. AI-accelerated workflows enable faster iteration, smarter systems, and more adaptive execution. This shift isn’t just technical; it’s cultural. It redefines what “impact” means for engineering teams and elevates the bar for innovation.
Today’s engineers are not just coding features; they are designing intelligent systems. The rise of agentic AI and multimodal models means that every product decision is now a systems-level decision. A search bar isn’t just a UI element; it is a predictive engine. A chatbot isn’t just reactive, it is a strategic interface.
This transformation demands new skills and new mindsets:
- AI fluency across the organization: From product to engineering to design, teams must understand how AI shapes user experience, data strategy, and ethical risk.
- Dual competency development: The most effective engineers are both builders of AI systems and power users of AI tools. This duality is a force multiplier.
- Ethical and secure design: As systems grow more autonomous, leaders must ensure they remain aligned, transparent, and secure.
For senior leaders, the mandate is clear:
- Invest in depth, not just access: Surface-level AI familiarity won’t drive transformation. Upskilling must go beyond prompt engineering to full stack understanding.
- Redefine velocity and value: AI compresses timelines and expands capabilities. The question is not “Can we build it?” but “Can we build it intelligently, ethically, and fast?”
- Champion tangible innovation: Theory is not enough. Leaders must incentivize shipped projects that demonstrate real-world application of AI systems.
The demand requires not just learning AI but launching initiatives with it.
Information technologies touch every segment of society, driving change and innovation across every industry. As organizations integrate new technologies to compete in the global environment, they require more computer software engineers to implement those new technologies. Today’s complex and competitive business environment demands that companies vigilantly ensure the reliability and integrity of computer systems to avoid costly and potentially catastrophic disruption. But, some of the mistakes from the past continue to be made. To ensure success and guard against failure, alert industries engage technically qualified experts with sound managerial judgment.
The World Economic Forum estimates that over 130 million jobs will be created globally in new professions, where demand for data scientists, software engineers and a myriad of roles requiring digital skills are growing rapidly. In addition, successful managers and leaders increasingly require a strong working knowledge of digital technologies, as well as 21st century leadership skills including the ability to be adaptable, innovative and creative.
This certificate offers what candidates need to know to understand fail-safe computer systems, both rapidly and prudently. The Software Engineering Certificate provides a foundation in technical concepts and design techniques, as well as management, organizational, governance, and teamwork approaches, for building software systems. The emphasis of this certificate is on implementing software engineering projects within cost and schedule by applying the most current proven and innovative practices that overcome the shortcomings of an undisciplined approach. The implications of AI on SW engineering will be covered as a fundamental topic throughout all of the courses.

The success rate of today’s digital initiative resembles the traditionally low success rate of IT Projects. We continue make the same mistakes.

The software industry is under intense pressure to deliver quality software. Because software production remains a labor intensive activity, the demand for large volumes of high quality software translates into a strong demand for qualified software engineers. This certificate is comprised of an appropriate balance of theoretical computer science foundations and IT management considerations that afford candidates with the means to remain abreast of developments in software engineering in the long term and practical applications that afford graduates the means to be operational in the short term.
Building on the lessons learned from the past is fundamental. Managers and software professionals who enroll in this certificate will become authorities on quantitative, rather than qualitative problem-solving methods, while learning to deal with a broad spectrum of enterprises—from small-scale to large complex projects.

Steps to Build an AI Agent